Self-tapping screws are used to quickly, simply, and stably connect thin plastic sheets, metals, light alloys, wood, and other ductile materials.
The threading of these screws is created following a particular geometry, to ensure a decent resistance to tearing and to anchor perfectly to the supports on which they are fixed.
Structure and Features of Self-Tapping Screws
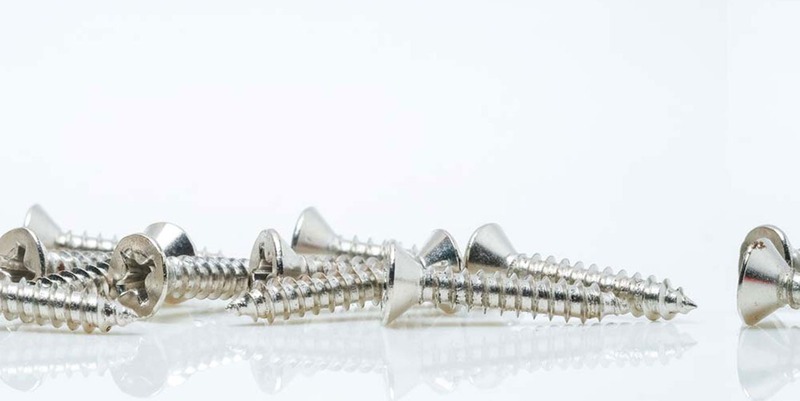
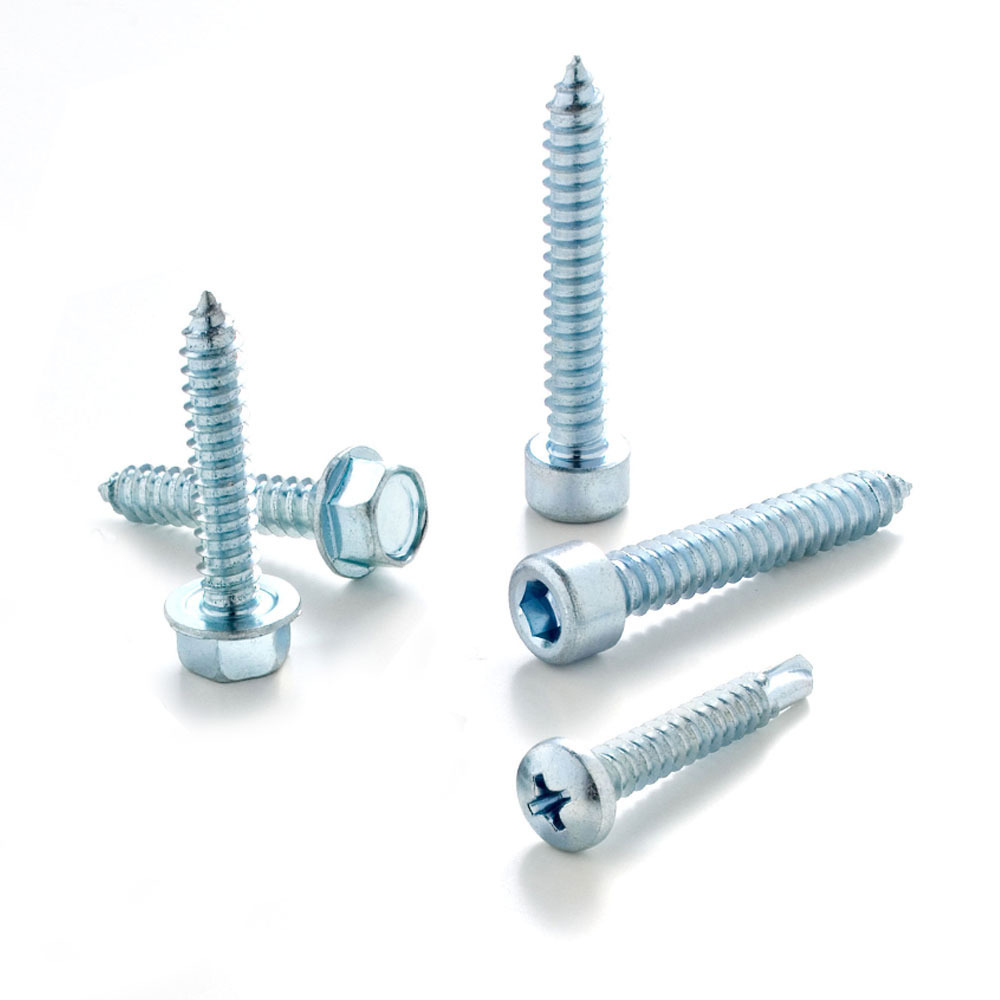
Self-tapping screws can have different configurations of the head, body, and tip, to better satisfy different types of fastening.
The types of head configurations for self-tapping screws are multiple and varied.
They are available on the market with different types of heads, the most common are:
- Hexagonal head
- Hexagonal head with flange
- Cylindrical head
- Countersunk head
- Flat countersunk head
- Countersunk head with dome
- Pan head
- Pan head with false washer
Depending on the purpose of use, it is also good to consider the type of drive to adopt, among the possible choices we can find:
- Hex socket, also called "Allen imprint"
- Phillips drive
- Torx drive
- Six-lobe drive
- Flathead screwdriver slot
The body is generally recognized for its conical structure, and the sharp tip, ideal for cutting into “soft” materials, and sharp edges. For particular applications, this type of product can also be found on the market with a flat tip.
Given the wide range of sectors in which they are used and the different types of parts to be fixed, self-tapping screws are available in different types of materials, among the most widespread are: steel and stainless steel.
Among the items we deal with, you will find:
Regarding the use and application of these items, to maintain the fastening of the parts even in case of vibrations, it is a good rule to always practice a pre-drilling. This must be slightly smaller than the diameter of the screw to allow the part to best fix the supports, in this way the screw will not have the possibility of "play".
Mistakenly, in many cases, self-tapping screws are confused with self-drilling screws. The latter, in fact, are recognized by the configuration of the tip, similar to that of a drill, with the capacity to drill without having to practice a pre-drilling.
Check out the dedicated section on our website by clicking here!
Or send us a request via email to verify the availability of the item you are looking for!
 Added to quote
Added to quote