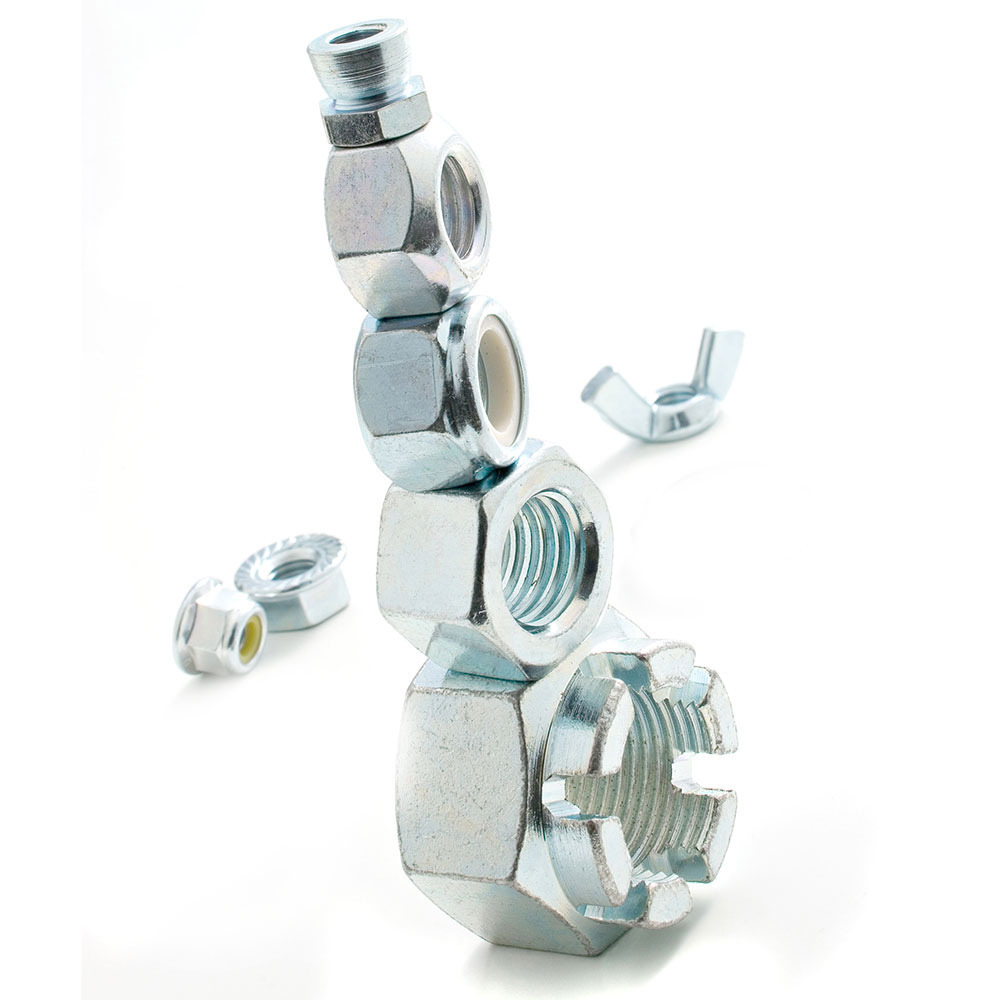
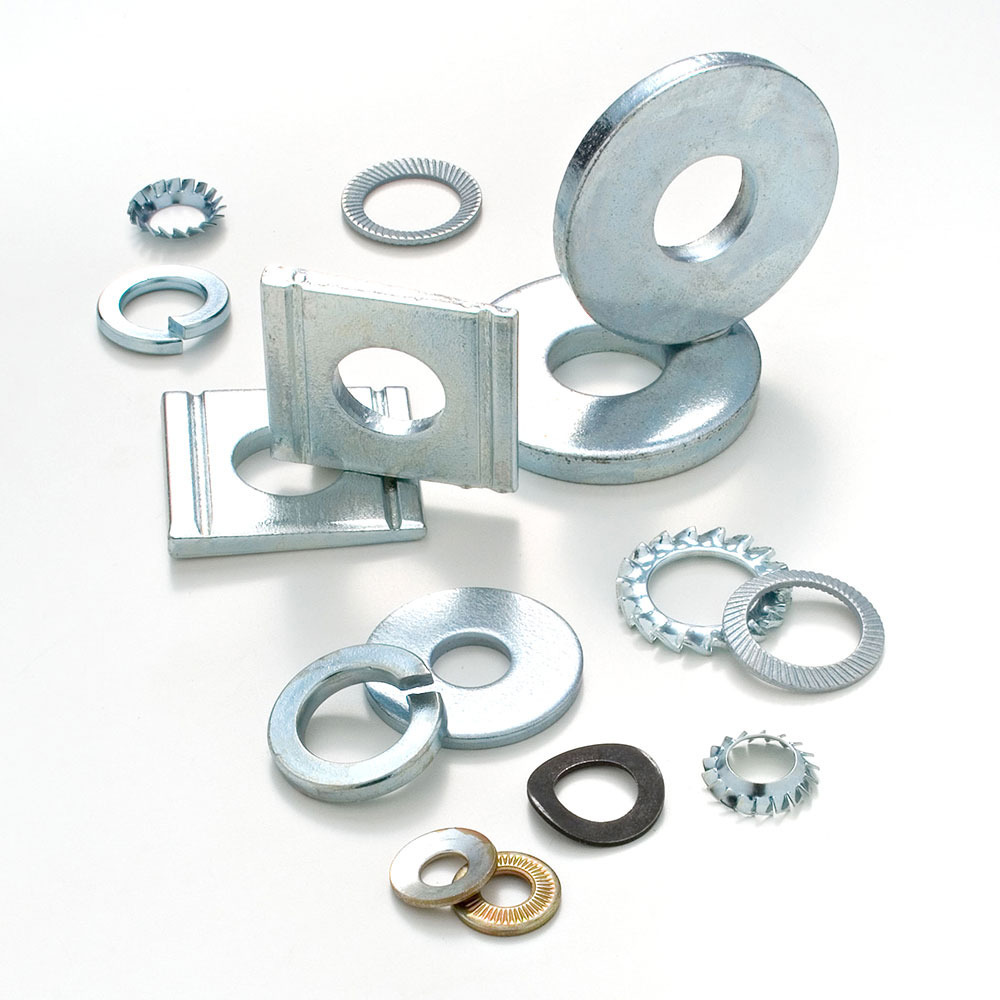
Over the years, road construction techniques have been refined, taking into account numerous factors such as road traffic, road alignment, or slope gradients. This evolution has seen an increasing use of appropriate fasteners and bolts capable of stabilizing the components used in road construction. In this article, we will analyze the screws and bolts used in such work and products, the material they are made of, and the certifications they must comply with.
 Added to quote
Added to quote